In an era where over 75% of our land areas are degraded, affecting over 3.2 billion people, the urgency for ecommerce businesses to lead in regenerative sustainability has never been clearer. Reports warn that without significant intervention, up to 95% of the Earth’s land could be degraded by 2050.
However, there’s a silver lining: regenerative sustainability initiatives present an unparalleled opportunity for ecommerce to not only halt but reverse environmental degradation.
In this article, we’ll go through what regenerative sustainability is and its benefits, why it matters in business, what that looks like in practice, and how to start making the shift to a more regenerative business.
What Is Regenerative Sustainability?
Regenerative sustainability emphasizes systems and practices that restore, renew, and revitalize their own sources of energy and materials. It aims to create processes that are not just sustainable but also beneficial to the environment, effectively contributing to the regeneration of ecosystems and communities.
This approach is rooted in the understanding that simply maintaining the status quo is insufficient to address the environmental crises we face. Regenerative sustainability seeks to actively improve ecological health, drawing inspiration from nature’s inherent ability to heal and sustain itself.
It incorporates principles like circular economy, where waste is minimized and materials are reused, and permaculture, which mimics the natural ecosystems in agricultural practices.
The three pillars of regenerative sustainability are planet, people, and governance. Key aspects of these pillars include:
- Restoring Ecosystems: Activities that help restore soil health, water quality, and biodiversity, reversing the damage done by industrial and agricultural practices.
- Building Resilience: Designing communities and systems that can adapt to environmental changes and shocks, thereby increasing their long-term sustainability.
- Promoting Social Equity: Ensuring that regenerative practices also support community well-being and fair access to resources, recognizing that environmental and social issues are interconnected.
- Innovating in Waste Reduction: Moving beyond recycling to envision a world where waste is designed out of systems from the beginning, often through the adoption of circular economy principles.
- Enhancing Well-being: Focusing on solutions that improve human health and happiness as integral components of sustainability.
Download our FREE ebook:

Regenerative sustainability is ambitious, but it offers a vision of a future where human activities can have a positive impact on the planet, healing past damages and creating a more flourishing and equitable world for generations to come. This framework can be applied in various fields, from agriculture and architecture to business and urban planning, making it a versatile and powerful approach to sustainability.
What is the difference between sustainable and regenerative design?
The concepts of “sustainable” and “regenerative” are closely related but have distinct differences in their approach and ultimate goals concerning human and environmental wellbeing, and social practices.
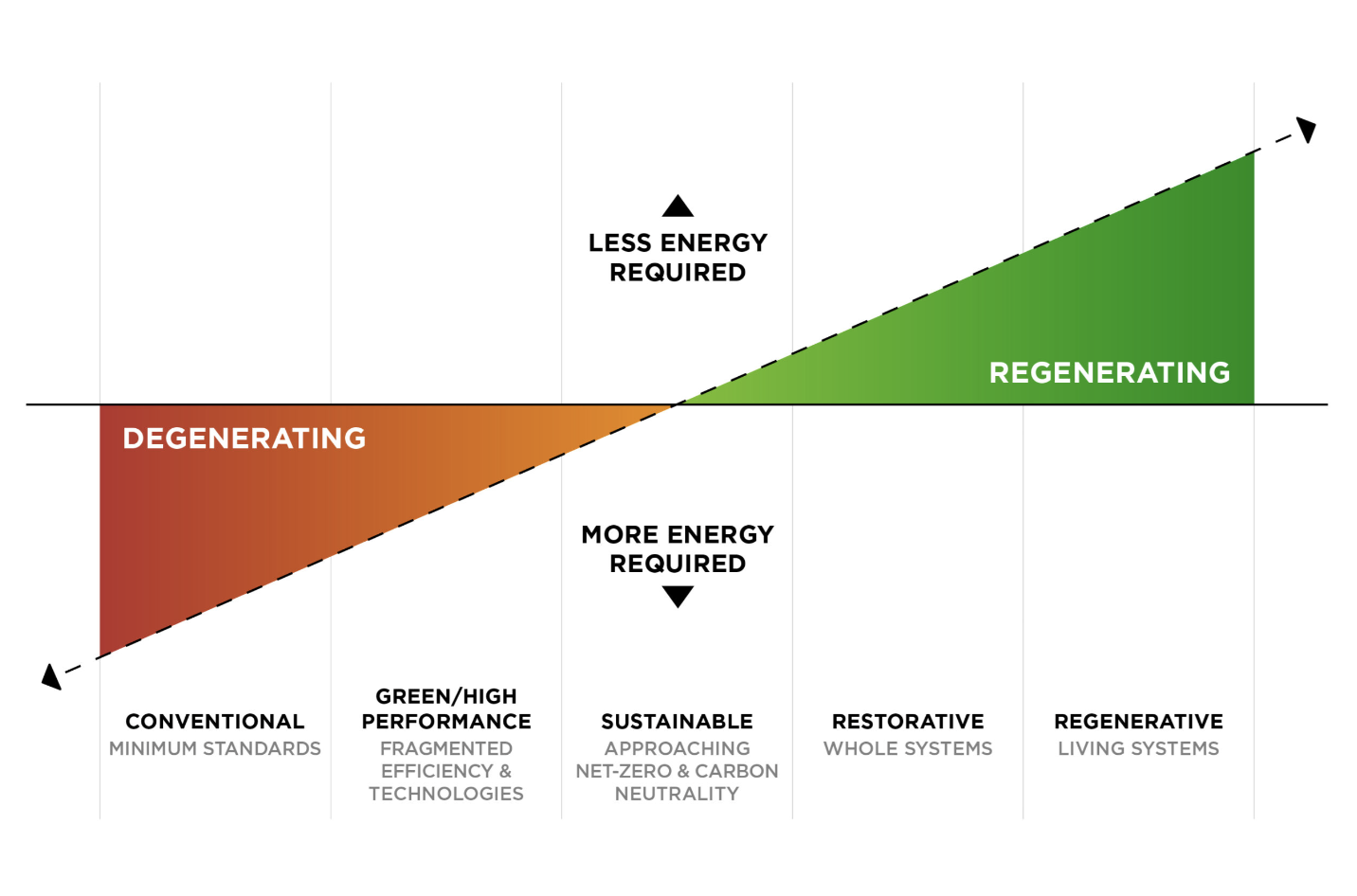
Sustainable Practices
Sustainability focuses on meeting current needs without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs. It emphasizes the conservation of resources, reducing waste, and minimizing the environmental impact of human activities. Sustainable practices aim to achieve a balance where the extraction of resources, energy use, and waste production are kept at levels that can be naturally replenished and absorbed by the Earth without leading to degradation or depletion of natural systems.
Regenerative Practices
Regenerative sustainability actively seeks to restore and revitalize natural systems through innovative and restorative practices. The goal is to create systems that are capable of regenerating themselves, improving their resilience, health, and vitality over time. With regenerative practices, organizations can leave it better than it was found, creating a net positive impact.
For example, a sustainable ecommerce business might work to reduce its carbon emissions. A regenerative business would not only reduce its greenhouse gas emissions but it would also remove emissions from the atmosphere as a result of operating business. This is possible through regenerative agriculture. Regenerative agriculture practices enhance soil health and biodiversity, significantly contributing to carbon sequestration by capturing atmospheric carbon dioxide and storing it in the soil. This relationship not only mitigates climate change but also improves agricultural resilience, creating a sustainable cycle of growth and renewal.
Benefits Of Regenerative Sustainability
The adoption of regenerative practices brings about profound benefits, directly addressing critical environmental and social challenges:
- Reduces deforestation by prioritizing products and packaging from sustainable sources.
- Improves nutrient management through the support of regenerative agricultural practices, enhancing soil health.
- Improves water and air quality by minimizing pollutants and investing in clean, renewable energy for operations.
- Enhances ecosystems by contributing to biodiversity and supporting ecosystem services.
- Actively restores habitats through initiatives that rehabilitate natural environments and wildlife.
- Produces nutrient-dense food by promoting and selling products from regenerative farming methods.
- Reduces harmful emissions with strategies like green logistics and carbon offsetting.
- Improves crop resilience to climate change by fostering agricultural diversity and soil health.
- Provides a systemic solution that benefits human health, animal welfare, the environment, and the economy, creating a sustainable loop of positive impacts.
- Contributes to a more sustainable and resilient future for communities and the planet as a whole.
By focusing on regenerative sustainability, ecommerce businesses can become catalysts for environmental restoration, human wellbeing and economic transformation. This approach not only mitigates the adverse effects of traditional ecommerce practices but also contributes actively to a healthier planet and a more equitable society.
Why Regenerative Sustainability Matters In Ecommerce
Integrating regenerative sustainability efforts into ecommerce operations is more than an ethical decision; it’s a strategic move that drives tangible business benefits. Let’s highlight the undeniable advantages for ecommerce businesses:
- Preferential brand perception: Nearly 80% of US consumers prefer brands labeled as “regenerative” over “sustainable”.
- Enhances revenue: Products with sustainability messages generate 6.4% higher revenue.
- Boosts customer recommendations: 63% of shoppers recommend products they consider less harmful to the planet.
- Influences purchasing decisions: 66% of consumers, and 75% of millennials, consider sustainability in their purchases.
- Increases brand loyalty: 68% of consumers are loyal to brands that share their values.
- Willingness to pay a premium: 70% of consumers are open to paying a 5% price premium for sustainable goods.
- Customer-driven sustainability strategies: The primary driver for companies adopting sustainability strategies is customer preference for sustainable products and services (41%).
- Meets and exceeds regulatory requirements related to sustainability.
These statistics underscore the critical importance of using regenerative principles for ecommerce businesses. By adopting regenerative practices, companies not only contribute positively to the environment but also leverage consumer trends that favor sustainability, ultimately leading to increased loyalty, revenue, and market differentiation.
Want to know where your business stands? Get your sustainability scorecard with our quiz:
Regenerative Agriculture
Conventional agricultural practices are no longer sustainable. With modern demands, they are inefficient and, as a result, are contributing significantly to habitat destruction. The agricultural industry also contributes to climate change, emitting considerable amounts of carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gasses such as methane.
Unfortunately, it gets worse.
Farming practices such as deforestation, excessive tillage, and the use of chemical fertilizers lead to environmental degradation. These deleterious effects are compounded by the lack of biodiversity in many modern farming systems, which increases the risk of disease transmission and crop failures.
Okay. That’s the bad news. How about some good news?
Regenerative agriculture and environmental design are two powerful tools in the fight against climate change and environmental degradation.

Regenerative agriculture is an agricultural system or set of practices that seek to restore degraded soils (a problem that costs the US economy $8billion a year), improve fertility, and increase biodiversity while also sequestering atmospheric carbon.
Recent research by the Rodale Institute suggests that switching to regenerative farming practices could sequester 100 percent of annual CO2 emissions. This would involve regenerative agricultural strategies incorporating cover crops, conservation tillage, rotational grazing, composting, agroforestry, and organic fertilizers.
Truly impressive stuff.
Further findings suggest that if all global pastures used for raising livestock switched to a regenerative model, 71 percent of produced greenhouse gasses (GHGs), some 37 GtCO2, could be sequestered.
Nice.
And the role of regenerative environmental design?
Like regenerative agriculture, regenerative environmental design goes beyond just being sustainable; it aims to create green spaces that actively enhance and promote the well-being of the surrounding ecosystem.
Together, these approaches offer a powerful solution for reducing the impact of human activity on the environment and work to achieve a more sustainable future.
Is regenerative farming sustainable?
Yes, regenerative farming is sustainable. It prioritizes soil health, biodiversity, and reduces synthetic inputs such as fertilizers and pesticides, which mitigate climate change and environmental degradation. Regenerative farming also emphasizes using natural and renewable resources, reducing reliance on synthetic and non-renewable inputs.
Does regenerative agriculture really work?
Sure, there are some creases to iron out. But using regenerative approaches to agriculture has shown promising results in improving soil health, increasing biodiversity, reducing erosion, and improving water quality.
Many farmers and agricultural organizations have already adopted regenerative practices and seen promising results. What’s more, as the discipline matures, further research is conducted, and practices improve, the potential benefits of regenerative agriculture are only expected to grow. And with the right support and investment, regenerative agriculture has the potential to revolutionize the farming industry and lead the way toward a more sustainable and resilient future.
Another way to achieve a sustainable future? By embracing sustainable ecommerce practices.
Regenerative Design
Like the agricultural sector, traditional construction practices are also responsible for significant environmental degradation. It is linked to several environmental issues, such as air and water pollution caused by harmful chemicals used during construction, and is responsible for 39% of energy and process-related carbon dioxide emissions.
Thankfully, regenerative design principles offer a solution to many of these issues.
Regenerative design enhances resource efficiency, reduces waste, and increases resilience to climate change impacts. For example, green roofs and bioswales reduce pollution runoff in urban areas while using recycled and sustainable building materials to reduce waste and limit the impact on natural habitats.
Regenerative design also encourages the use of renewable energy sources, such as wind power and solar, to reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
The concept of regenerative design also includes using eco-friendly building materials and designing buildings and structures to minimize their impact on the environment and maximize their contribution to natural systems. This can include using sustainable, non-toxic, and locally sourced materials and designing energy-efficient structures incorporating features like rainwater harvesting systems.
Challenges with regenerative design
Implementing regenerative design principles comes with some challenges, such as:
- Resistance to change. Many established businesses and organizations may resist change and hesitate to embrace regenerative design practices.
- Cost. Some regenerative design practices require an upfront investment, which can be a barrier for some businesses and organizations.
- Lack of awareness. Many people may not be aware of the principles of regenerative design and the benefits that it can bring.
- Limited availability of skilled professionals. There may be a limited number of professionals with the necessary skills and expertise to implement regenerative design principles.
- Local regulations and building codes. Some local regulations and building codes may not be conducive to implementing regenerative design practices, which can create barriers to adoption.
Opportunities with regenerative design
As we’ve seen, regenerative design is all about using nature’s systems and processes to design buildings and infrastructure that use resources efficiently, produce less waste, and are better equipped to handle the challenges of climate change. In fact, co-building a regenerative economy could unlock up to $26 trillion in financial value and create over 65 million new green jobs globally by 2030.
This global scale presents your business with tremendous growth opportunities—26 trillion of them, to be exact.

Steps For Adopting A Regenerative Mindset
If you’d like to move toward a regenerative business model, then start thinking beyond your greenhouse gas emissions. To adopt a regenerative mindset when implementing green initiatives:
- Assess your current practices. Understand your own supply chain and which areas produce the highest carbon emissions. Investigate how your supply chain impacts social systems, as well as ecosystems. Begin by conducting a supply chain audit. For more details and professional recommendation, EcoCart’s Life Cycle Analysis will highlight your biggest areas of improvement along your supply chain to get you started.
- Collaborate with like-minded organizations. Partner with other businesses and organizations that share your values and work towards regenerative sustainability.
- Experiment and iterate. Try out new regenerative practices and be willing to adapt and improve them over time. Embrace a culture of experimentation and learning.
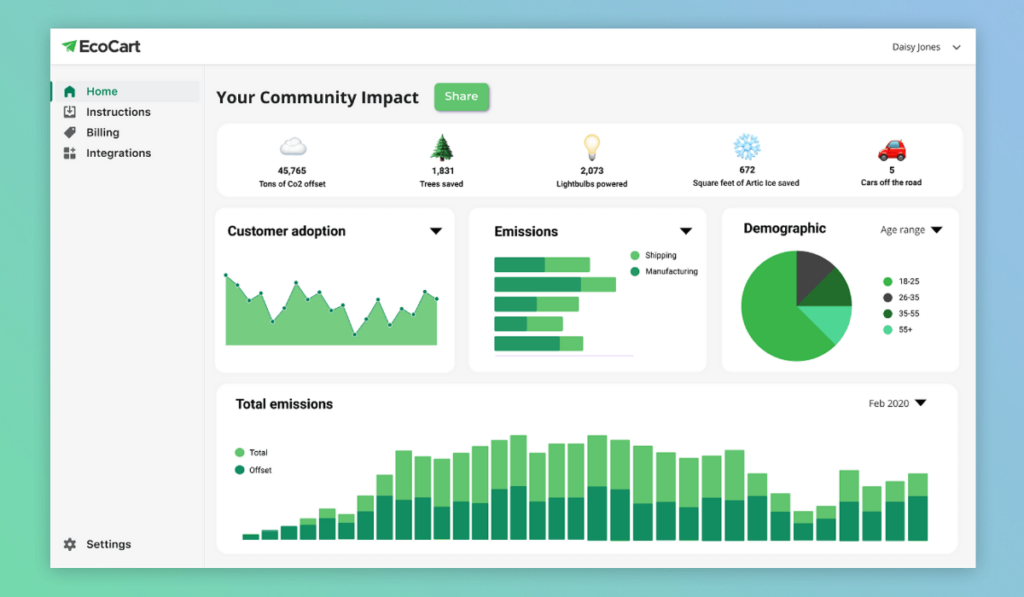
- Measure and track progress. Set goals and metrics to measure the impact of your regenerative practices. Use this data to identify areas for improvement and celebrate successes. EcoCart’s Sustainability Insights Dashboard tracks your greenhouse gas emissions in real time so that you know exactly how your business is performing.
Best Regenerative Business Practices
No matter the industry or niche your business falls under, it’s time to start making a difference with these impactful regenerative sustainability practices:
- Regenerative materials and waste. Look for ways to use environmentally friendly materials and minimize product manufacturing and packaging waste. This means selecting materials that don’t rely on fossil fuels and demonstrate regenerative actions in their production and manufacturing progress.
- Energy use. Identify areas of your business operations that use the most energy. Read our guide to a business energy audit for instructions on how to do this. Consider implementing energy-saving practices like turning off equipment when not in use, using natural light whenever possible, and investing in renewable energy sources.
- Circular economy. Embrace a circular economy model emphasizing product reuse, recycling, and composting.
- Sustainable suppliers. Collaborate with sustainable suppliers who prioritize sustainability and ethical practices, and can demonstrate regenerative outcomes.
- Employees and customers. Spread awareness and education about sustainability initiatives within your business, including how your employees and customers can contribute.
Conclusion
As we work towards a more sustainable future through initiatives like regenerative sustainability, it’s essential to recognize that every industry has a strong role to play in sustainable development. This regenerative paradigm shift will take time as businesses work to evaluate and improve their supply chains. EcoCart’s carbon offsetting checkout widget helps businesses mitigate their carbon footprint by compensating for emissions they can’t immediately eliminate, bridging the gap until they can implement regenerative actions.
Make your ecommerce site more sustainable with EcoCart—request a demo today.