The numbers don’t lie: carbon dioxide emissions rose 90 percent between 1970 and 2004, and by 2019, the concentration of CO2 in Earth’s atmosphere hit an 800,000-year high. This rapid escalation has resulted in rising global temperatures, caused increasingly sporadic and severe weather events, and is disrupting ecosystems on a global scale.
To combat these threats, Carbon Capture, Utilization, and Storage (CCUS) technology has emerged as a promising solution. This guide explores carbon capture’s role in mitigating climate change and its potential in our global climate response.
What Is Carbon Capture and Why Is It Important?
The idea behind CCUS involves capturing carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions from sources, such as power plants and industrial processes, and preventing them from entering the atmosphere. Once theoretical, with recent developments, the technology behind this process has seen a rapid evolution and is now a reality. CCUS technologies are now operating at 35 commercial facilities, with an annual capture capacity of 45 Mt CO2. Capable of capturing over 90 percent of CO2 emissions from power and industrial facilities.
Learn more: What Does It Mean To Be Carbon Neutral?
How Carbon Capture Works
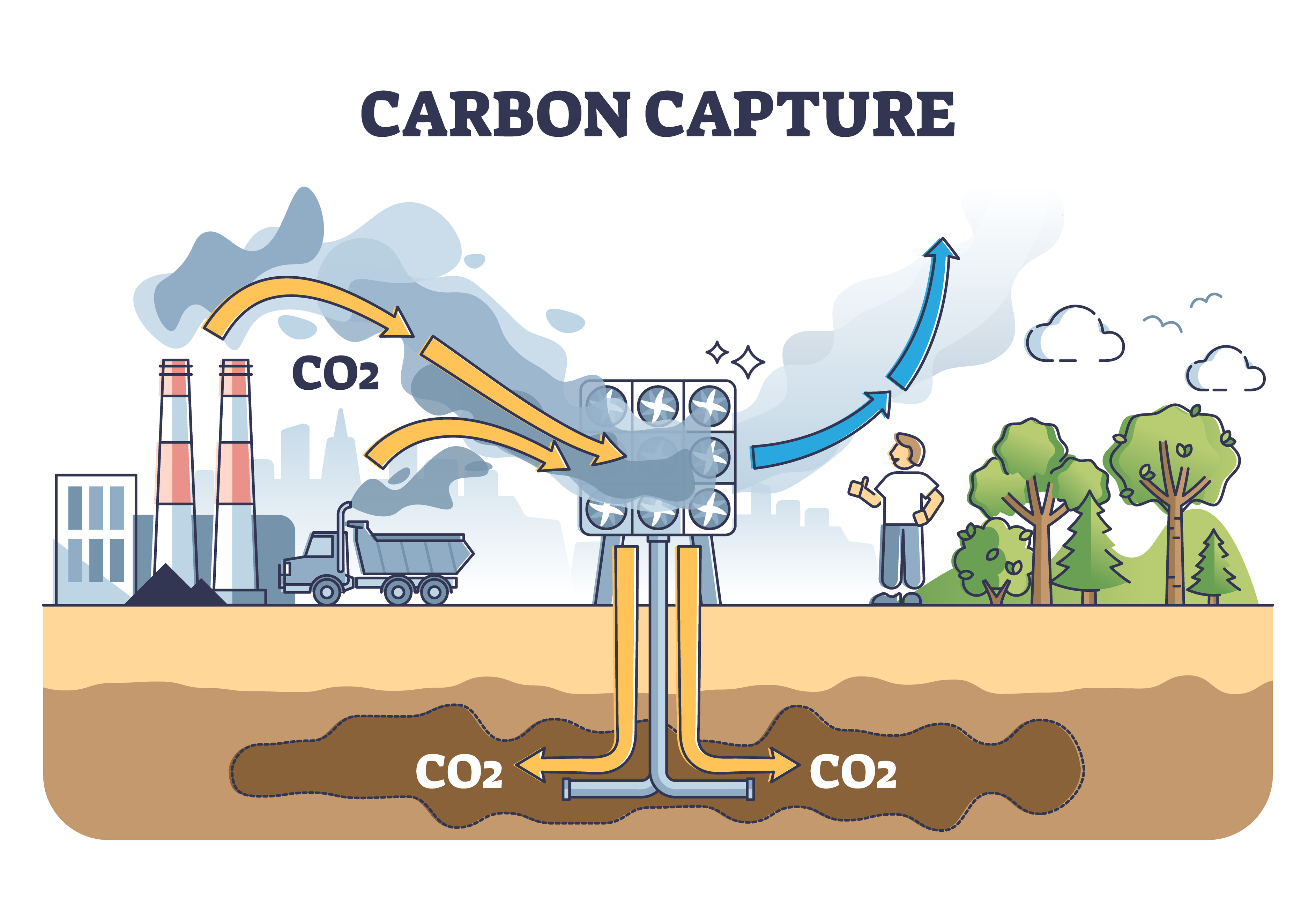
The process of carbon capture entails three primary steps: capture and storage or utilization—Carbon Capture and Storage (CCS) or Carbon Capture and Utilization (CCU). As hinted at in their acronyms, the first step, carbon capture from emission sources, is common to both processes. Post-combustion, pre-combustion, and oxyfuel combustion are the three main technologies used to capture CO2 emissions, functioning by either trapping CO2 before or after fossil fuels are burned or by burning the fuel in oxygen to simplify CO2 capture.
Carbon Capture and Storage (CCS)
Storage, also called “sequestration,” involves a kind of return to roots for CO2. It’s injected deep underground into geological formations—typically, depleted oil and gas fields or deep saline aquifer formations, often several kilometers beneath the Earth’s surface—where it’s securely stored rather than being released into the atmosphere.
Carbon Capture and Utilization (CCU)
CO2 isn’t always stored; in carbon capture, utilization, and storage (CCUS), captured CO2 can be converted into valuable products such as biofuel, chemicals, building materials, and synthetic fuels.
For instance, the cement industry, responsible for nearly 7 percent of global emissions, could dramatically reduce its carbon footprint with CCU by employing techniques like CarbonCure. This method involves injecting recycled CO2 into fresh concrete during mixing. The CO2 then chemically transforms into a mineral, enhancing the concrete’s compressive strength and enabling a reduction in cement content. This approach not only prevents carbon from reaching the atmosphere but also develops a CO2 market, improving the economic feasibility of carbon capture.
How Does Carbon Capture Reduce Climate Change?
As CO2 emissions surge and efforts to keep global warming below 1.5 degrees Celsius intensify, key organizations such as the International Energy Agency (IEA) and International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA) emphasize that rapidly expanding CCUS technologies are critical in combating climate change.
The IEA underscores the importance of CCUS, noting that it could both decrease global CO2 emissions by almost a fifth in the context of the alarming 41 billion tons of annual emissions and simultaneously cut the cost of tackling the climate crisis by 70 percent.
Why Carbon Capture is Important for Climate Change
According to a U.N. report, simply halting CO2 emissions isn’t enough—we need to actively remove approximately 17 billion tons of CO2 from the atmosphere each year to reverse the impacts of climate change.
In the face of this challenge, CCUS plays a significant role. As per the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC), over half of the models in their Fifth Assessment Report deem CCUS crucial to limit global warming to 2 degrees Celsius above pre-industrial levels.
However, while CCUS can contribute to achieving net-zero emissions, more is needed to yield the negative emissions required to offset climate change. As the National Academies highlights, an additional ten gigatons of CO2 must be removed annually by the middle of this century. Therefore, CCUS, which has the potential to contribute to 14 percent of the required global greenhouse gas reductions by 2050, is a vital piece of the solution but only part of the answer.
The Pros and Cons of Carbon Capture
Let’s explore the key benefits, drawbacks, and environmental and social implications of carbon capture technology:
Advantages
- Carbon capture not only possesses many potentials, but it is already significantly reducing the amount of CO2 released into the atmosphere from industrial processes and power generation.
- Carbon capture is currently the only practical way to achieve deep decarbonization in specific heavy industries like cement and steel production.
Limitations
- Carbon capture technologies can be expensive to implement and maintain, and there are often substantial costs associated with transporting and storing the captured CO2.
- The carbon capture and storage process requires substantial energy, which can lead to increased emissions if the energy is not sourced from renewable or low-carbon sources.
Environmental and Social Impact
- While CO2 is generally stored safely underground, there is a risk of leakage that could harm local environments.
- Working with captured CO2, especially at high concentrations, can pose safety risks, requiring strict protocols to ensure worker safety.
Current State of Carbon Capture Technology
The CCUS market is evolving rapidly. Traditional methods like forestation are useful, but novel technologies such as Bioenergy with Carbon Capture and Storage (BECCS) and Direct Air Capture and Carbon Storage (DACCS) need scaling.
The good news? In the last two decades, there’s been considerable innovation, including $4 billion in publicly funded projects and an upsurge in patents, notably from China. And encouragingly, CCUS-equipped industrial plants operating today are designed to capture about 90 percent of CO2 from flue gases, with 61 new facilities added globally in 2022.
The Costs of Carbon Capture
As of 2020, the target cost for commercially viable carbon capture was set at $50 per ton of CO2. Less than three years later, this seems achievable, with scientists reporting a record low cost of $39 per ton using newly developed techniques.
However, as of right now, costs vary. Post-combustion capture typically ranges from $40-$90 per ton, influenced by fuel type, plant size, and capture technology. Meanwhile, pre-combustion capture costs about $60 per ton from integrated gasification combined cycle (IGCC) power plants, with research aiming to reduce this to $30.
Carbon Capture in the Energy Sector
Fossil fuel power plants, including coal and natural gas, are leading CO2 emitters. Thankfully, their carbon footprints can be drastically reduced by incorporating CCUS technology, primarily through post-combustion capture, with existing power plants having the capacity to be retrofitted with this technology, reducing emissions without the need to build new infrastructure from scratch.

Examples of Carbon Capture Projects
The progress in the carbon capture field is encouraging, with nearly 200 large-scale facilities in operation or under construction as of 2022. Notable examples include Texas’s Petra Nova project, which hosts the world’s most extensive post-combustion carbon capture system, and Charm Industrial. This San Francisco-based startup uses biomass waste for CO2 removal. Also, Saskatchewan’s Boundary Dam 3 CCS Facility is the world’s first fully integrated carbon capture facility on a coal-fired power plant.
Learn more: Verified Carbon Offsets.
Carbon Capture Policy and Regulations
Government policies and incentives are instrumental in advancing CCUS technologies. In the US, the 45Q tax credit is a pivotal policy, offering financial incentives for each metric ton of carbon captured and either stored or used, consequently reducing costs for companies employing CCUS. There are also regulations under consideration requiring natural gas-fired power plants to install carbon capture technology, in line with US efforts to decarbonize the power sector.
And looking toward the future, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) is expected to propose new standards for power plants based on their potential to reduce emissions via CCS. This follows a Supreme Court decision allowing plant-specific rules and the Inflation Reduction Act, providing tax credits for carbon capture and hydrogen.
Capturing a Better Future
Carbon capture is a vital tool against climate change, a technology that’s advancing, becoming more economically viable, and broadening its reach.
Yet, the path to the Paris Agreement goals is steep, requiring not just new technologies but innovative use of existing ones. Solutions like EcoCart embody this approach, intertwining economic advantages with sustainability and consumer engagement.
Ready to contribute to this sustainable path? Discover how EcoCart can seamlessly integrate a carbon-neutral shipping option into your online store, aligning your business with the future of carbon capture and sustainable practices.



